| Guideline: Guideline On Problem Prioritization |
 |
|
Relationships
| Related Elements |
|---|
Main Description
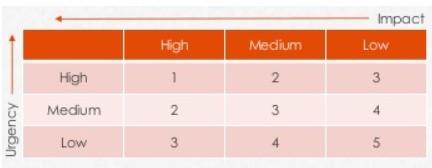
Parameters For Problem Prioritization Every ticket should be allocated an individual priority derived from its perceived urgency and impact. The coding system described below is used to prioritize problems. This combines the impact with urgency to give an overall priority level. The higher the urgency and impact, the higher is the priority assigned.
Problem prioritization must also consider the severity of the problems. Severity indicates how serious the problem is from a service or customer perspective as well as from an infrastructure perspective. For example,
Priority Levels Blocker Critical function/system of an application unavailable or inoperable or severely degraded causing major impact on service delivery and Client’s business. Major sections of Client application or multi customer locations are impacted. No alternative, workaround or bypass is available. Critical A critical business process/function/system is impaired, suffering or degraded, causing impact on a part of service delivery or on a dedicated critical business activity. Minority of Client application or one Client location is impacted. Inefficient or non-acceptable alternative, workaround by-pass is available. Normal A non-critical business process/function/system is affected, suffering or degraded, causing impact on a non-critical part of service delivery or on a non-critical dedicated business activity. Only a few individual application users are impacted but the functionality is available for all. Acceptable and efficient alternative, workaround or bypasses are available. Non-Critical / Minor
These are problems with less severity or low impact incident which does not require immediate attention. |